티스토리 뷰
레이아웃(layout)
화면을 구성하는 형태 (요소들의 배치 형태)
다양한 레이아웃을 사용하여 요소들의 배치 형태를 결정 가능
각 레이아웃을 지원하는 객체 사용하여 레이아웃 적용 가능
- BorderLayout, FlowLayout, GridLayout, CardLayout 등
BorderLayout
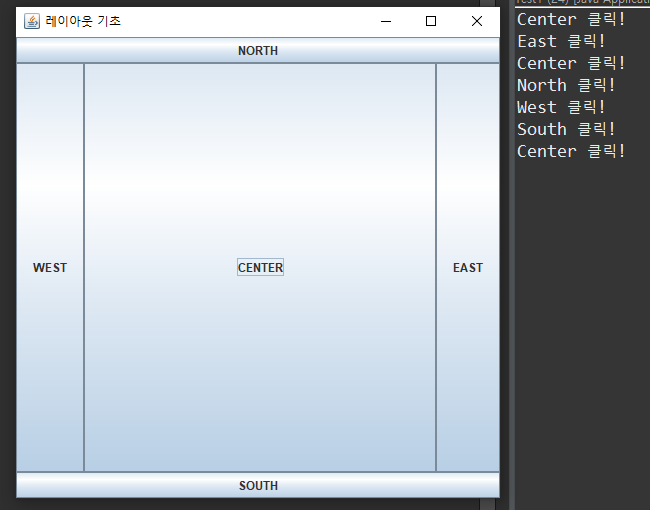
- JFrame 객체의 기본 레이아웃으로 대상 컨테이너의 동, 서, 남, 북, 중앙 5개의 영역으로 분할하여 컴포넌트를 배치한다.
=> 별도의 설정이 없을 경우, 기본적으로 BorderLayout이 적용되어 있다.
- 배치할 영역을 지정하는 경우, add() 메서드의 두번째 파라미터로 BorderLayout.XXX 상수를 사용하여 위치 지정이 가능하다. "North", "Center" 등의 문자열도 사용 가능하나 오타로 인한 오류 가능성이 있다.
- 한 영역 당 1개의 컨테이너나 또는 컴포넌트 배치 가능, 두 개 이상 컴포넌트 등을 배치할 경우 마지막에 추가된 대상만 표시되고 나머지는 뒤에 가려진다.
package layout;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class Test1 {
public Test1() {
showFrame();
}
public void showFrame() {
JFrame f = new JFrame("레이아웃 기초");
f.setBounds(200,200,500,500);
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// 버튼 부착
JButton btnC = new JButton("CENTER");
JButton btnN = new JButton("NORTH");
JButton btnE = new JButton("EAST");
JButton btnW = new JButton("WEST");
JButton btnS = new JButton("SOUTH");
// 이벤트 연결 (5단계)
f.add(btnC, BorderLayout.CENTER);
f.add(btnN, BorderLayout.NORTH);
f.add(btnS, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
f.add(btnW, BorderLayout.WEST);
f.add(btnE, BorderLayout.EAST);
btnC.addActionListener(e -> System.out.println("Center 클릭!"));
btnN.addActionListener(e -> System.out.println("North 클릭!"));
btnE.addActionListener(e -> System.out.println("East 클릭!"));
btnW.addActionListener(e -> System.out.println("West 클릭!"));
btnS.addActionListener(e -> System.out.println("South 클릭!"));
f.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Test1();
}
}
4단계 방식
btnC.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println(e.getActionCommand());
if(e.getSource() == btnC) {
System.out.println("center 버튼");
} else if(e.getSource() == btnE) {
}
}
});ActionListener listener = (e) -> {System.out.println(e.getActionCommand() + "버튼 클릭됨");};
btnC.addActionListener(listener);
btnE.addActionListener(listener);
btnW.addActionListener(listener);
btnN.addActionListener(listener);
btnS.addActionListener(listener);
레이아웃 변경
- 기존에 설정된 레이아웃을 변경하여 다른 형태로 컴포넌트 배치 가능
- 컨테이너 객체 생성 시 생성자에 레이아웃 객체를 전달하거나 컨테이너 객체의 setLayout() 메서드를 호출하여 레이아웃 변경이 가능하다.
FlowLayout
- 컨테이너 내의 컴포넌트들을 흐름에 따라 자연스럽게 배치하는 레이아웃으로 좌 -> 우, 상 -> 하 방향으로 컴포넌트들을 차례대로 배치한다.
- 하나의 컨테이너 내부에 여러 개의 컴포넌트 배치가 가능하다(위치 지정 불가)
- JPanel(패널) 의 기본 레이아웃
public void showFrame() {
JFrame f = new JFrame();
f.setBounds(800, 300, 300, 300);
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT);
// f.setLayout(flowLayout);
// 위 두 문장을 한 문장으로 결합
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
// 버튼 5개 생성
JButton btn1 = new JButton("Button 1");
JButton btn2 = new JButton("Button 2");
JButton btn3 = new JButton("Button 3");
JButton btn4 = new JButton("Button 4");
JButton btn5 = new JButton("Button 5");
// BorderLayout과 달리 FlowLayout은 컴포넌트 배치 시 별도의 위치 지정 불필요
f.add(btn1);
f.add(btn2);
f.add(btn3);
f.add(btn4);
f.add(btn5);
f.setVisible(true);
}
GridLayout
컴포넌트를 테이블(표) 형태로 배치하는 레이아웃으로 행, 열 구조, 배치되는 컴포넌트의 크기가 균등하다.
=> GridBagLayout 사용 시 크기가 다른 행, 열 구조 편성 가능
- 첫 행의 좌측 열부터 우측 열 방향, 다음 행의 좌측 열부터 우측 열 순으로 배치
- BorderLayout과 같이 컨테이너 크기가 변경되면 컴포넌트의 크기만 변경되고 컴포넌트 배치 위치는 변경되지 않는다.
GridLayout gridLayout = new GridLayout(3, 2);
f.setLayout(gridLayout);위의 상태에서 버튼 삽입하면 아래처럼 된다

행, 열 선택, 수평간격, 수직간격 지정 시
GridLayout gridLayout = new GridLayout(3, 2, 10, 30);
f.setLayout(gridLayout);
'배운 것 기록 > java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| JOptionPane (0) | 2022.07.27 |
|---|---|
| JTextField, JPanel (0) | 2022.07.27 |
| Event (0) | 2022.07.20 |
| Swing (0) | 2022.07.18 |
| DecimalFormat, MessageFormat 클래스 (0) | 2022.07.16 |
